Optical Illusion
An optical illusion is a visual phenomenon that tricks the brain into perceiving something different from what is actually present.
This occurs when the brain processes visual information in ways that differ from reality, often leading to a misinterpretation of the size, shape, color, or position of objects. Optical illusions work by exploiting the way our eyes and brain interpret visual cues.
For example, illusions might involve contrasting colors or patterns that make one part of an image seem to move or change, or they may use perspective to create a sense of depth where none exists.
These illusions are often designed to exploit the brain's assumptions and expectations about the visual world, resulting in images that appear to bend, twist, or shift when they are static.
Some common types include geometric illusions, color illusions, and motion illusions, all of which challenge the way we typically perceive visual stimuli.
Must Try: Within 9 Seconds Spot The 3 Differences in this Mom and Child Image
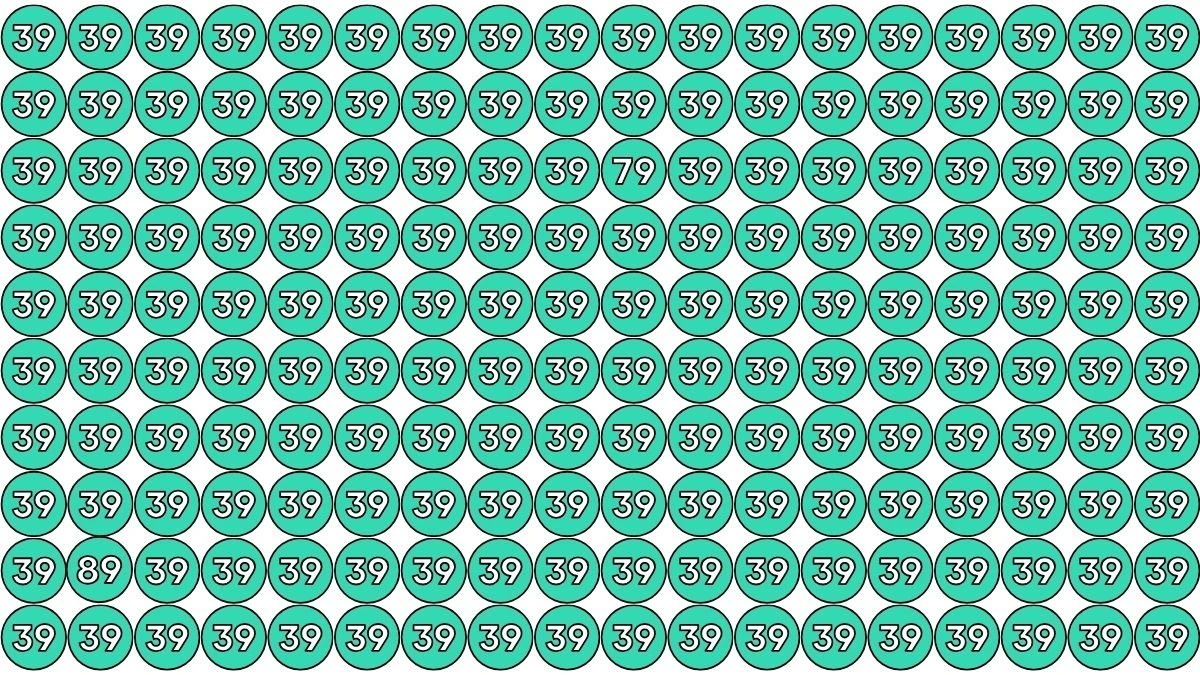
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Are You A Genius? Within 6 Seconds Spot The Inverted 73 among Inverted 37s

Are You A Genius?: Within 5 Seconds Spot The Letter M among Ws
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Are You A Genius? Within 6 Seconds Spot The Inverted 73 among Inverted 37s - Solution
The inverted "73" is placed in the image near the center, surrounded by the inverted "37s." It can be found in the fourth row from the top and the ninth column from the left.
While the majority of numbers in the grid are "37" flipped upside down, the "73" is the only number that stands out due to the reversed order of its digits.
This subtle change in orientation makes it the only anomaly among the seemingly identical numbers. To solve this optical illusion, it's crucial to carefully scan the grid and focus on the direction of each number.
The challenge lies in quickly identifying this one exception, testing both your attention to detail and visual processing speed.
This exercise is designed to sharpen your ability to spot visual differences in a dense and repetitive pattern.